Corporate Information
Vietnam Market Overview and Analysis
Vietnam’s economy demonstrated robust growth in 2024, with GDP expanding by 7.09%, exceeding both the National Assembly’s target of 6-6.5% and the 2023 growth rate of 5.05%. This performance positions Vietnam among the fastest-growing economies in Southeast Asia, outperforming regional peers like Singapore, Malaysia, and Thailand. Projections indicate that Vietnam’s digital landscape, the fastest growing in the region, will reach US $45 billion by 2025. The government’s proactive efforts in national digital transformation are expected to further accelerate this growth, making Vietnam an increasingly attractive market for digital innovation and investment.
In 2024, Vietnam attracted US$38.23 billion in registered foreign direct investment from 114 countries and territories. Disbursed FDI reached a record high of approximately US$25.35 billion, a 9.4% year-on-year increase, signaling strong investor confidence. This investment comprised 3,375 new projects totaling US$19.73 billion, US$13.96 billion in adjusted capital for 1,539 ongoing projects (a substantial 50.4% rise), and over US$4.54 billion in capital contributions and share purchases. The surge in disbursed FDI and new projects underscores Vietnam’s continued attractiveness as a key investment destination. Furthermore, Vietnam’s population of over 101 million, coupled with a large, skilled, and cost-effective workforce, enhances its appeal as a leading destination for global businesses expanding within the ASEAN region. Singapore currently leads investment in Vietnam, followed by South Korea, China, Hong Kong, and Japan
Key Advantages of
Incorporating Your Business in Vietnam
Government Policies that Foster Support
The Vietnamese government offers various investment incentives, particularly attractive to foreign investors, including tax incentives like reduced corporate income tax rates and tax holidays for sectors aligned with national development goals, such as high-tech, large-scale, or socially important industries. Additional incentives include import duty exemptions for qualifying projects and land rental fee exemptions in areas with challenging socio-economic conditions or for projects requiring relocation due to urban planning or environmental concerns. Special incentives are also available for projects with significant foreign direct investment (FDI) and technology transfer potential.
Optimizing Business Processes
Vietnam ranks third in the Emerging Asia Manufacturing Index 2024, reflecting its economic stability and resilience. The manufacturing sector grew by 8% in 2022, tripling its growth from 2020 to 2021. The country is also emerging as a potential innovation hub, with startups projected to secure US$5 billion in funding between 2023 and 2025. The government, known for its stable leadership, is committed to improving business policies, labor laws, and infrastructure, positioning Vietnam as a leading ASEAN destination for foreign direct investment.
Ideal Free Trade and Tax Agreements
Since joining the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2007, Vietnam has become a committed global trade partner, entering into numerous Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) and Double Tax Avoidance Agreements (DTAs). Vietnam’s FTAs, including key agreements like the RCEP, CPTPP, and EVFTA, provide trade advantages across regions such as ASEAN, Europe, and the Asia-Pacific. Additionally, Vietnam has signed over 80 DTAs, helping to eliminate double taxation by reducing or exempting taxes for residents of partner countries. These agreements are essential for foreign investors to understand and leverage for optimal tax and trade benefits.
Prime Business Location
Vietnam benefits from a politically stable environment, with a government deeply committed to ensuring safety and enforcing comprehensive laws against terrorism and cybersecurity threats. Its strategic location in Southeast Asia positions it as a crucial hub for international trade, providing well-connected shipping routes to major markets like the US, Europe, and other Asian regions. This strategic advantage has led to lower international freight costs and a high degree of trade openness, fostering Vietnam’s role in the global economy.
Strategic Industrial Parks,
Exporting Processing Zone and Economic Zones
Vietnam’s Industrial Parks (IPs) are strategically planned areas designed for production of industrial goods and provision of services for industrial production, playing a crucial role in the country’s economic growth and attracting foreign investment. IPs, located in all the North, Central, and South regions, are hubs for manufacturing, offering top-notch infrastructure, logistics, and attractive tax incentives, making them ideal for foreign investors looking to optimize production and profits. An export processing zone (EPZ) is a concentrated industrial zone specializing in the production of export goods, provision of services for export goods production, and export activities, and also has specified geographical boundaries. There are only four EPZs in Vietnam, out of which two are fully occupied. An Economic Zone (EZ) is a specific zone model in Vietnam. An EZ is characterized by a favorable investment scheme of a local/regional government within a specified geographical area. This zone may be organized into functional areas, including non-tariff areas, bounded areas, industrial areas, entertainment areas, tourism areas, residential areas, administrative areas, as well as an export processing area. There can be many IPs established in an EZ and locating in these IPs may help manufacturing businesses enjoy a lower level of tax.

Essential Licenses for Starting a Business in Vietnam
To establish a new company as a legal entity in Vietnam, you are required to obtain two primary licenses: the Investment Registration Certificate and the Enterprise Registration Certificate. These documents are essential for incorporation and serve as the foundational approvals needed to legally operate your business within the country.
Beyond incorporation, specific operational licenses are necessary, depending on the nature of your business activities. Sectors such as health services, pharmaceutical manufacturing, medical equipment, hospitality, food and beverage, real estate, transportation, film production, water production, education, wine production and retail, multi-level marketing, cosmetics and supplements, promotional services, printing production, bodyguard services, etc. Each requires a one-time operational license after your company is set up. Additionally, importing special products like mining materials, weapons, chemicals, and medical supplies mandates an import license, which may need to be renewed annually in accordance with prevailing regulations.
Primary Requirements and Considerations
to Start a Business in Vietnam
Capital Requirements
Starting a business in Vietnam generally requires no minimum capital, but sufficient funds are needed until the business is self-sustaining. We recommend USD 25,000 to 40,000. For sectors like education, finance, real estate, insurance, and banking, capital assessment by the Department of Planning and Investment is often required.
Overseas Ownership Conditions
In Vietnam, foreign investors can own 100% of a company in most sectors, except for advertising, tourism, and oil, gas, and mining, which require a Vietnamese joint venture. For sectors not covered by local or WTO regulations, approval from the relevant ministry is needed.
Registering Business Address
In Vietnam, each business must have a registered business address. In some sectors such as trading, service,… using virtual offices instead of physical office is accepted. However, the Department of Planning and Investment of some provinces are strict in accepting virtual offices as business addresses. In this case, businesses must use a physical address to register.
Categories of Companies in Vietnam
Vietnam, situated next to the East Sea, is a crucial maritime hub on the global stage. With 29 of the world’s 39 major maritime routes passing through this region and one of the top ten global routes navigating the South China Sea, it handles between 250 and 300 ships daily. The East Sea’s strategic location underscores its significant role in regional and global security, maritime, and economic transport.

Limited Liability Company (LLC)
A Limited Liability Company (LLC) in Vietnam is ideal for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). It can be established with 1 to 50 corporate(s) or individual(s). The LLC offers flexibility in transferring capital contributions, making it a practical choice for businesses seeking ease of ownership transfer and a straightforward establishment process.

Joint Stock Company (JSC)
A Joint Stock Company (JSC) is suited for medium to large businesses, requiring between 3 and unlimited shareholders, either corporate or individual. JSCs are advantageous for companies looking to transfer shares with relative ease and those interested in listing on the stock exchange. This structure supports significant growth and public investment opportunities.
Branch Office
A Branch Office is suitable for investors who have been active for at least 5 years and whose operations align with those of their home country. This setup only requires a head of the branch, making it a streamlined option for businesses wanting to operate locally without the need for extensive capital or additional shareholders.

Representative Office (RO)
A Representative Office (RO) is designed for investors who have been operational for at least 1 year. It does not permit direct business activities or require capital investment. The RO must have a designated head, making it a cost-effective solution for market research and establishing a presence without engaging in commercial transactions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Corporate Information

Vietnam Corporate Information
Skip to:
Vietnam Corporate Information
Heart of South East Asia
Vietnam is located right next to the East Sea – a commercially important “link bridge” on the world maritime map, of the 39 maritime routes currently operating in the world, there are 29 routes passing through the East Sea territory. Of the 10 largest maritime routes in the world, the South China Sea region has one route passing through and 5 related routes, on average, 250-300 ships travel through the East Sea per day. In terms of strategic location, security, maritime and economic transport, the East Sea is very important for many countries in Asia in particular and the world in general.
Global Production Base


Alternative Option Investment
The output values of many Vietnamese products and industries, such as semiconductor, optoelectronic, information, and communication products account for more than 25% of the Asia Pacific market. Vietnam is invested by very big corporations such as LG, Samsung to set up production plants, from which products are exported to all over the world. A series of investors also came together to join the chain of production and supply of goods. Agriculture and tourism are also a strength of Vietnam. Investors are tending to move from heavy industry to agriculture, tourism and services because Vietnam has numerous islands and land and tourism resources.
Effect of Vietnam FTA
Vietnam has 16 Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) that have been or are being negotiated, helping to open the door of more than 60 economies, including 15/20 countries of G20. With a strong Supporting Industry, Vietnam is an ideal environment for investors.
In conclusion, the international ranking reports show that Vietnam’s business environment remains as excellent as it is now. Looking toward the future, Vietnam will continually create a better, friendlier environment, more conducive to business.


GENERAL
| Location of Jurisdiction | South East Asia |
| Official Language | Vietnamese |
| Political Stability | Excellent |
| EU Savings Tax Directive Applies | No |
| Tax on Offshore Profits | Yes |
| Disclosure of Beneficial Owner | Yes |
| Submit Audited Accounts | Audit for financial statements is required for FDI company |
| Time to Incorporat | 4-8 weeks |

CORPORATE
| Type of Company | Limited Company, Company limited by shares, Partnership Company, private business. |
| Type of Law | Law on enterprise |
| Allowed Business Activities | An entity-level certificate/license may be required for certain regulated businesses (e.g. financial institutions, construction, Education, Law, Accounting & Auditing, Insurance, Wine…) |
| Local Registered Office/ Agent Required | Yes |
| Change of Domicile | No |
| Shelf companies Available | No |
| Language of Documents | Vietnamese |
| Name of Company | Vietnamese and English also |
| Corporate Seal | A corporate seal is mandatory |

DIRECTOR
| Eligibility | Any person of any nationality |
| Minimum Number of Directors | 1 (at least ONE nature person) |
| Disclosure to Authorities & Public | Yes |
| Residence Required | May reside anywhere |
| Local Director Required | No |
| Location of Meetings | Anywhere |

COMPANY SECRETARY
| Secretary Required | No |
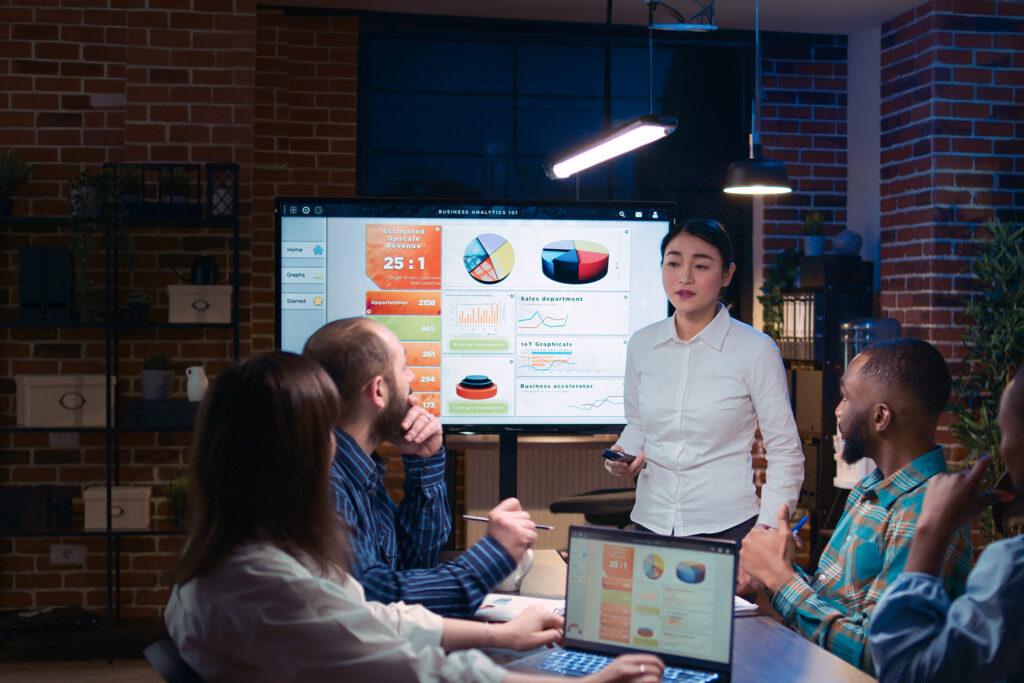

Limited Liability Company (LLC)
- 1 - 50 corporate(s) or individual
- Suitable for SMEs
- Easy to transfer capital contribution(s)
- Easy and swift establishment

Joint Stock Company (JSC)
- 3 to unlimited corporate(s) or individual(s)
- Suitable for medium and large businesses
- Easy to transfer shares
- Be listed on the stock exchange

Branch Office
- Investor is active for 5 years
- Operation matches home country
- Only head of the branch is required

Representative Office (RO)
- Investor is active for 1 year
- No business activities allowed
- No capital requirements
- Required head of the representative office