Taiwan’s lowest bracket tax rate for individuals (5%) makes it one of the lowest rates in the world.
However, many expatriates and businesses in Taiwan may wonder what Taiwan Tax rate they fall under.
Throughout this guide, we will cover the basics of the Taiwan tax system. Moreover, we will also go over the various tax rates an individual may fall under and how to pay your tax in Taiwan.
Taiwan Tax System: The Basics


Taiwan divides its taxes into local and national levels. The Ministry of Finance collects national taxes from individuals and businesses for the various tax categories we will cover in the next section.
Local governments, however, use regional tax offices to collect taxes that relate to building, land, and acquisitions.
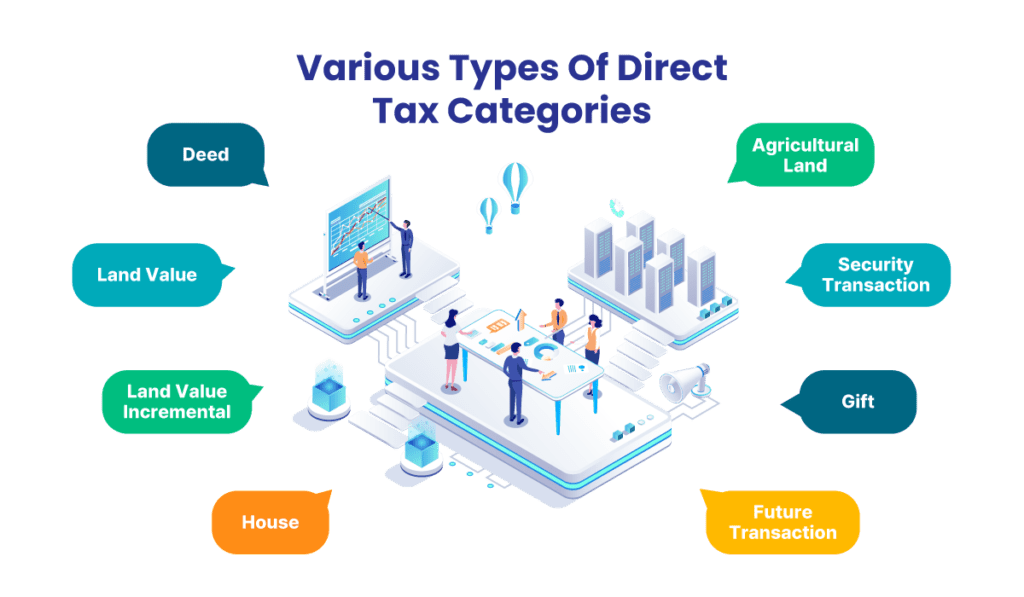
Otherwise, Taiwan’s government has various types of direct tax categories that include:
- Deed
- Land value
- Land value incremental
- House
- Agricultural land
- Security transaction
- Gift
- Future transaction
Taiwan also has a list of other indirect taxes on the national and local levels.
Different Rates for Individuals and Businesses in Taiwan
Throughout this section, we will define the various tax rates that Taiwan has for companies and resident- and non-resident aliens. Also, each section will cover basic information that everyone should understand about these rates and who must pay them.
Income Basic Tax: Taiwan Tax Rate for Expats
To fall under income tax in Taiwan for a tax resident, you will need to reside within Taiwan for 183 days in a tax year. The individual income tax rate for foreigners in Taiwan who are considered tax residents is between 5% and 40%, depending on their bracket.
However, non-resident aliens who have been in Taiwan under 183 days in a given year must also pay a flat rate of 18%. That means if an individual makes over NTD$2,420,000 per year and doesn’t live in Taiwan for over 183 days, they will pay 18% instead of the 30% rate for tax residents.
There is an exception for aliens who visited Taiwan for business trip and stayed in Taiwan under 90 days in a tax year. If his/her salary was paid in his/her home country, the salary is exempted for income tax filing.
Taiwan Corporate Tax Rate



Taiwan’s corporate tax rate is 20% which is lower than most of advanced countries. Moreover, for-profit entities must report all of their business income from onshore and offshore sources. The deadline of corporate income tax return is May 31st every year.
If a business’ income is from overseas, they may deduct the taxes they pay from the country they made money in (foreign tax credit). The foreign tax credit cannot exceed the tax amount if the Taiwan income tax applied.
Taiwan has signed the tax treaty with more than 30 countries. You may also seek the advice from tax expert to avoid the double taxation.
Withholding Tax in Taiwan
Instead of an individual paying a tax, the payer, usually an employer, will pay withholding tax. Whenever an employer pays an employee, they will deduct or withhold a certain amount from their paycheck for tax purposes.
For residents, withholding rates in Taiwan range between 0% and 10%, depending on your income source. At the same time, non-residents must pay 18–21% for income sourced from Taiwan.
For general salaries, residents must withhold 5% and non-residents 18%.
Value Added Tax (VAT) In Taiwan
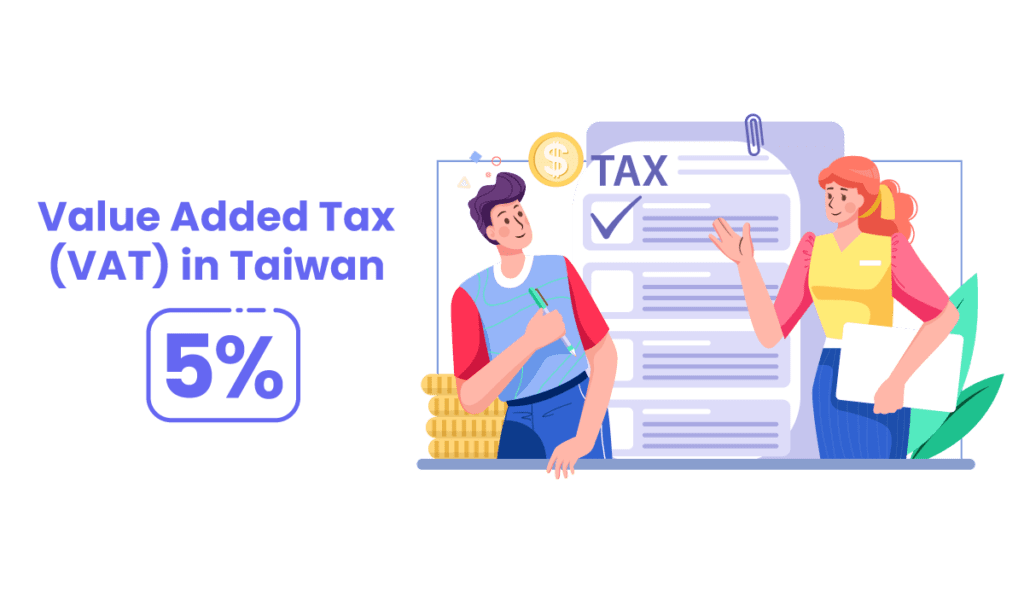


Value-added tax (VAT), otherwise known as business tax, are taxes imposed on the sale of services and goods or the services provided within Taiwan throughout the various stages of the supply chain.
The current VAT rate is 5% for general products and services in Taiwan.
Officials calculate the VAT in Taiwan on imported goods by the regular rate (5%), and gross value after the following taxes and fees are applied if applicable:
- Tobacco
- Alcohol
- Commodity
- Custom duty
Securities Transaction Tax
Individuals must pay taxes for all securities transactions, except for specific tax-exempt securities and government bonds. Shares and options are subject to a rate of 0.03% and transactions for futures 0.000001% to 0.6%.
However, the rates for securities transactions will depend on the selling price for an individual’s security.
Taiwan Luxury Tax
Whenever a dealer sells a private jet, helicopter, or passenger vehicle valued at NTD$3,000,000 or over, they are subject to a luxury tax rate of 10% per sale. Moreover, high-end furniture sellers must pay a rate of 10% of sales involving preserved wildlife products that are worth NTD$500,000 or more.
Land Value Increment Tax
Whenever anyone sells land, they are subject to a land value increment (LVIT) tax. The tax rate on the land is determined based on an increase of its government-assessed value. The special LVIT tax is 10%, whereas progressive rates range between 10% and 40%.
Taiwan Property Tax
Individuals will assess real estate annually and determine a tax rate based on their officially assessed value. The tax rate for land value ranges between 1–5.5%, commercial properties 3–5%, and non-commercial properties 1.2–3.6%.
Taiwan Stamp Tax
Whenever individuals handle contractual agreements and deeds of sales of moveable properties or real estate property, they must pay Taiwan’s stamp tax. Rates for deeds of real estate transactions and contractual agreements are 0.01% of the contract price.
Whereas the rate for deeds for movable properties is NTD$12 per piece, and receipts of payments are 0.04% of the amount received.
Filing and Paying for Taxes in Taiwan
Fortunately, tax filing in Taiwan is not tricky. You have a couple of options: visiting a tax office and speaking to a specialist or using Taiwan’s e-filing. To pay for your taxes, you can use the following payment methods:
- Convenience stores: 7-11, Hi-life, OK Mart, and Family Mart
- Wire transfer
- Payment cards (debit or credit)
- Paper check payments
- Cash
Make Sure That You Are Set Up for Tax Season in Taiwan
While Taiwan has many tax categories, the Taiwan tax rate for expats is lower than many countries in most categories. Moreover, Taiwan has a convenient system for foreign residents to pay taxes.
Explore our site for more information on the Taiwan tax system and services to help you set up a business in Taiwan.
FAQs
How does one become a tax residency in Taiwan, and how is the duration of stay in Taiwan calculated?
Tax residency in Taiwan is established if
(1) you spend 183 days or more in Taiwan within a calendar year, or
(2) you possess Taiwanese nationality, maintain a registered household in Taiwan, and stay for at least one day in a calendar year.
It's important to note that the day of arrival in Taiwan is not included in the count, but the departure day is included. Keeping track of your days in Taiwan through passport stamps is advisable.
When is the deadline for Taiwan income tax payments?
The deadline for Taiwan income tax payments is June 3rd, with penalties for late payments applicable thereafter.
What factors determine a company's obligation of Taiwan income tax?
Companies headquartered in Taiwan are subject to corporate income tax on both domestic and international income (global income taxation). Companies with headquarters outside Taiwan are taxed solely on income generated within Taiwan.
What constitutes the business tax system in Taiwan?
Taiwan employs two business tax systems:
Value-added tax (VAT): Applied to general industries, it is levied at each stage of production, distribution, or sale of a product or service.
Non-value-added tax: Applicable to specific regulated industries such as banks and clubs.
What is the extent of vat and applicable tax rate?
VAT in Taiwan covers:
(1) Sales of goods or services within Taiwan (including services purchased abroad and used within Taiwan).
(2) Imported goods or services.
The current VAT rate for general goods or services is 5% in Taiwan.
Related Posts
- Taiwan Tax Filling: Everything You Should Know About Taiwan’s Tax Filling
- Taiwan Withholding Tax Guide For Non-Resident Payees
- The Ultimate Guide to Business Tax in Taiwan
- What Foreigners Need To Know About Tax Filing Deadline In Taiwan
- A Detailed Guide for Taiwan Tax Residency